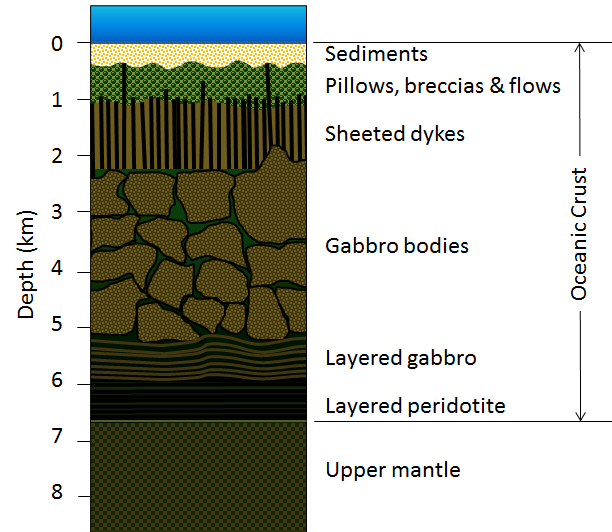
The only exception are the crests of the spreading centres where new ocean floor has not existed long enough to accumulate a sediment cover.
Main source of sediment on ocean floor.
Silicious silica rich and calcareous calcium containing.
Deep ocean sediment containing at least 30 biogenies material is called.
Continental shelf 300 feet continental slope 300 10 000 feet abyssal plain 10 000 feet abyssal hill 3 000 feet up from the abyssal plain seamount 6 000 feet.
Sediments on the ocean floor only rarely come from a a single source.
Pelagic sediment is composed of clay particles and microskeletons of marine organisms that settle slowly to the ocean floor.
Researchers calculate that there are 3 37 10 8 cubic kilometers of sediment on the world s ocean floor.
The following features are shown at example depths to scale though each feature has a considerable range at which it may occur.
Terrigenous sediment is derived from land and usually deposited on the continental shelf continental rise and abyssal plain.
Most deposits are a mixture of and particles.
Pelagic sediment or pelagite is a fine grained sediment that accumulates as the result of the settling of particles to the floor of the open ocean far from land.
Ocean basin ocean basin deep sea sediments.
This sediment is composed of clay particles and microskeletons of oceanic organisms that sink slowly through the water column to the ocean floor.
Some of these organic.
2 types of ooze.
The main source of terrigenous sediments.
New global analysis reveals amount of sediment on the ocean floor.
Some may call this sediment biogenous sediment and this sediment roughly covered 75 of deep seafloor and one of the most important constituents of ocean sediments.
These particles consist primarily of either the microscopic calcareous or siliceous shells of phytoplankton or zooplankton.
Sediment thickness in the oceans averages about 450 metres 1 500 feet.
The ocean basin floor is everywhere covered by sediments of different types and origins.
It is further contoured by strong currents along the continental rise.
Marine sediment any deposit of insoluble material primarily rock and soil particles transported from land areas to the ocean by wind ice and rivers as well as the remains of marine organisms products of submarine volcanism chemical precipitates from seawater and materials from outer space.